They consume vast tracts of content, cost a packet to train and graft well past normal office hours. Junior lawyers have much in common with generative artificial intelligence. Galling, then, for the former to face pay stasis — Slaughter and May is freezing their salaries at £150,000 for now — while more spending is being thrown at AI.
Expect the machines to continue shouldering more of the workload. Fusty image notwithstanding, lawyers have been deploying tech for nearly a century: dictaphones in the 1950s and two decades later the clunky red UBIQ that enabled case law search without recourse to libraries.
Today tech is corralled to zip through documents, conduct due diligence, summarise cases and even draft simple ones. It can handle matters like conveyancing or litigation; one of England’s newest law firms uses AI to prepare “polite” debt chasing letters for just £2.
Nor is it all just grunt work. LexisNexis’s Lex Machina — no relation to this column — helps predict the outcome of litigation cases based on past behaviour of courts, counsel and judges. A&O Shearman’s antitrust AI tool works out which jurisdictions require regulatory filings to be lodged and what information they will need before drafting the necessary requests for any missing data.
A few years down the line all this may look as laughably quaint as the Dictaphone. AI boosters see it plugging gaps in the constitution, highlighting potential legal action — think well-informed ambulance chasers alerting you to a breach of copyright, say — or even acting as judge. Parties input their grievances, the model spits out a resolution.
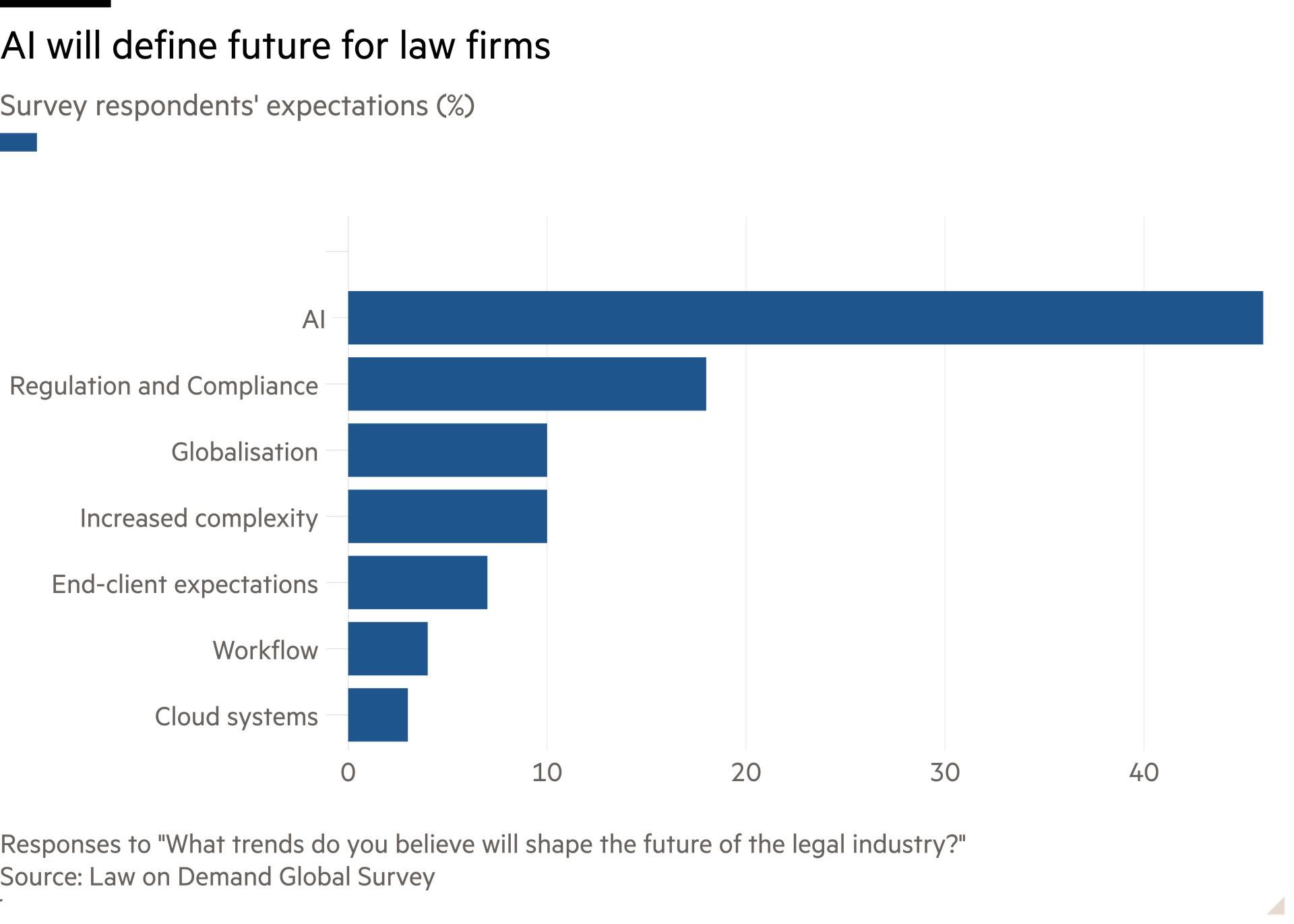
For now, the case for junior lawyers remains. Finances stack up. Hourly billing rates vary hugely, but assume £600-£700 at a magic circle firm. Applying the lower end to 1,500 billable hours leaves several times their salary to be tipped into the partners’ pot.
Today’s juniors are also tomorrow’s seniors: succession planning relies on an intake of young blood. Algo-generated reports still need human oversight; that usually entails at least some degree of amending too. The Panglossian view on AI applies in law too: if it is easier to launch cases, more people will do so, thus expanding the pie.
But there’s a more fundamental role for humans. AI, with tentacles in every sphere of business and society, requires its own rule book. That is a massive undertaking, spanning ethics, intellectual property, privacy and much else besides. Budding legal bigwigs still have a case.